Lesson Title: Core Modules of SAP ERP: A Practical Overview with PepsiCo Examples

Lesson Description:
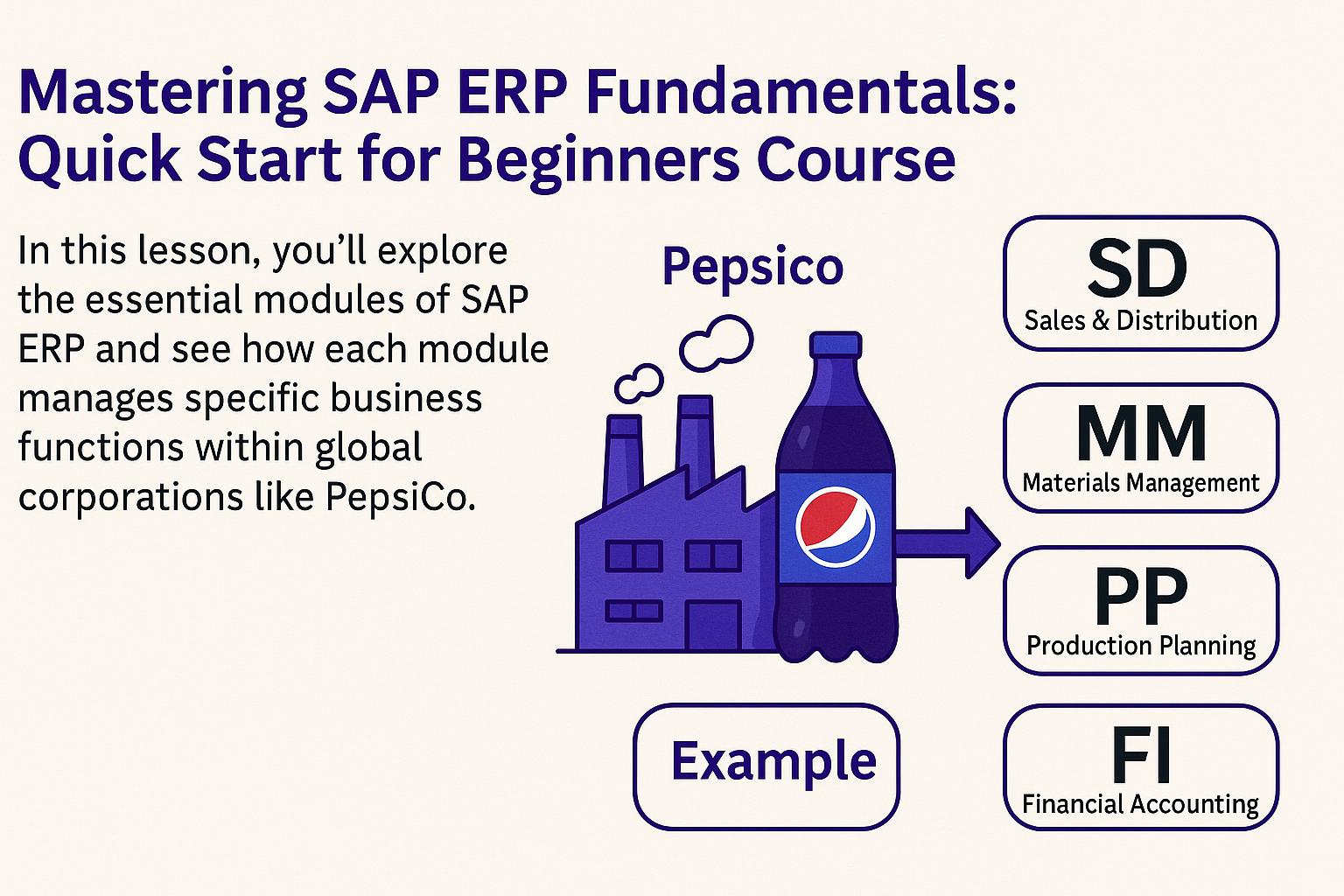
In this lesson, you’ll explore the essential modules of SAP ERP and see how each module manages specific business functions within global corporations like PepsiCo. Using practical, real-world examples from PepsiCo’s operations, you’ll gain a clear understanding of how modules like Sales & Distribution (SD), Materials Management (MM), Production Planning (PP), Financial Accounting (FI), and others integrate seamlessly, ensuring efficient business processes and accurate, real-time data sharing.
Lesson Learning Objectives:
-
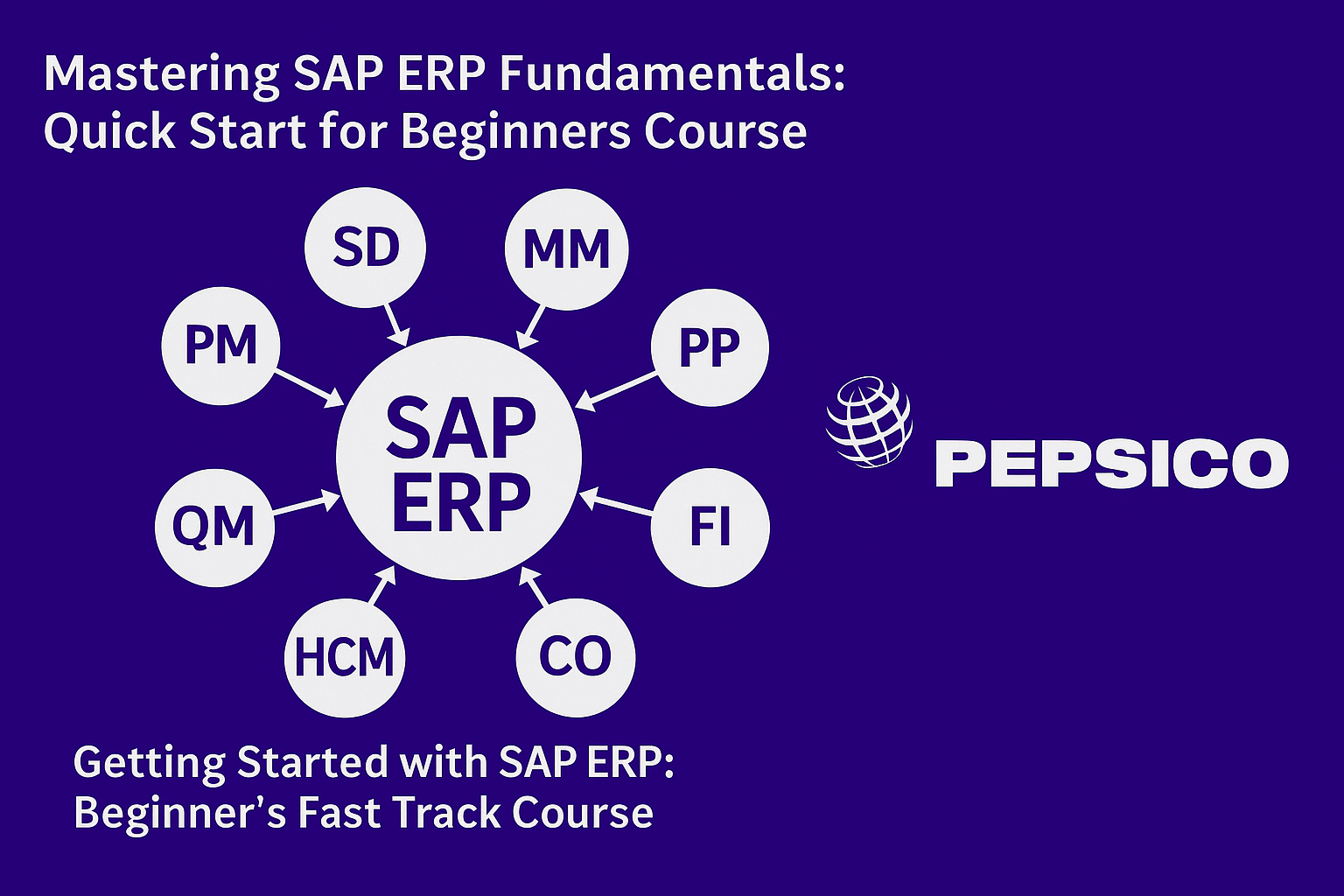
Clearly identify and define the core SAP ERP modules.
-
Understand how each module operates within a global business context, illustrated by PepsiCo examples.
-
Appreciate how module integration ensures efficient business operations and improved decision-making.
Terminology:
-
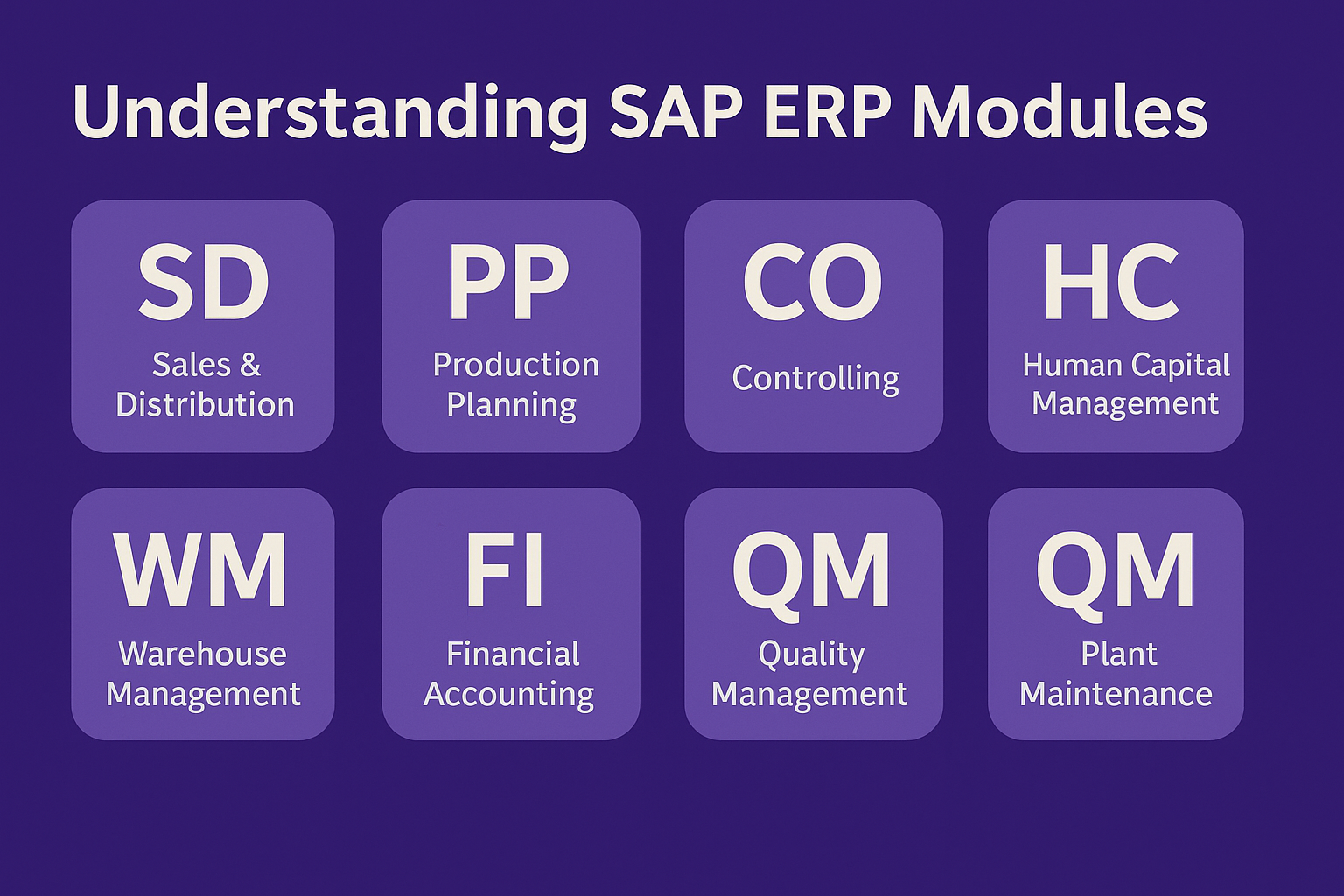
SD (Sales & Distribution): Manages sales processes, from order entry to customer delivery.
-
MM (Materials Management): Oversees procurement and inventory management.
-
PP (Production Planning): Plans and controls manufacturing processes.
-
FI (Financial Accounting): Records and reports on financial transactions.
-
CO (Controlling): Provides internal cost analysis and budgeting tools.
-
HCM (Human Capital Management): Manages employee-related data and HR processes.
-
WM (Warehouse Management): Tracks and optimizes warehouse storage and logistics.
-
QM (Quality Management): Ensures product and process quality through testing and compliance measures.
-
PM (Plant Maintenance): Manages equipment maintenance and repairs, ensuring smooth production.
Lesson Key Points:
✅ Sales and Distribution (SD):
SD handles the entire sales lifecycle, from capturing customer orders to delivery and billing. For example, when a supermarket orders 1,000 cases of Pepsi, the SD module confirms stock availability, processes the order, arranges shipment, and issues invoices, ensuring revenue accuracy and customer satisfaction.
✅ Materials Management (MM):
MM oversees procurement, inventory management, and supply chain coordination. If Pepsi needs more corn syrup for beverage production, MM generates a purchase order, tracks incoming materials, updates inventory levels, and automatically triggers reorders when supplies are low. This prevents production delays due to shortages.
✅ Production Planning (PP):
PP aligns manufacturing processes with demand forecasts. At Pepsi, if forecasts indicate that 500,000 bottles must be produced next month, PP creates detailed production schedules, ensures ingredients from MM are available, and updates inventory as products are completed, optimizing factory efficiency and stock management.
✅ Financial Accounting (FI):
FI meticulously records all financial activities and generates accurate financial statements. For every sale, purchase, or expense, FI logs detailed entries, updating the general ledger in real-time. Pepsi relies on FI to maintain clear, accurate financial records, tracking profits, assets, liabilities, and ensuring transparency and compliance.
✅ Controlling (CO):
CO provides detailed internal cost and profitability analysis. At Pepsi, CO calculates the precise production costs for products by combining data from MM and PP and compares it against revenue captured in FI, highlighting profitability per product or region. Additionally, CO tracks departmental budgets, enabling managers to make informed cost-saving and pricing decisions.
✅ Human Capital Management (HCM):
HCM handles comprehensive workforce management—from employee records, time-tracking, and payroll to benefits administration. At PepsiCo, HCM ensures tens of thousands of employees worldwide receive accurate and timely payments. Employee time data seamlessly integrates with FI for payroll expenses, facilitating efficient HR management.
✅ Warehouse Management (WM):
WM meticulously manages warehouse logistics, tracking the precise location of inventory items, optimizing storage and product picking. When Pepsi prepares a shipment, WM directs warehouse personnel exactly where to pick products, updates real-time inventory levels, and coordinates closely with MM, resulting in faster fulfillment, fewer errors, and efficient logistics.
✅ Quality Management (QM):
QM incorporates rigorous quality control steps into operational processes. Pepsi employs QM to perform mandatory quality inspections on incoming ingredients and finished products, preventing defective batches from reaching customers. Any quality issues detected automatically trigger corrective actions, ensuring only high-quality products leave Pepsi’s facilities.
✅ Plant Maintenance (PM):
PM schedules and records preventive maintenance and repairs for equipment and machinery. For instance, Pepsi’s bottling equipment undergoes regular maintenance logged in PM. If unexpected equipment failures occur, PM logs the incident, tracks the repair process, and coordinates with MM for necessary spare parts, significantly reducing downtime and maintaining smooth operations.
✅ Integration Across Modules:
The strength of SAP ERP lies in the seamless integration between modules. For instance, a customer order placed via SD can automatically initiate production planning in PP if inventory is low, MM manages material procurement, WM organizes storage and shipment, FI records the transaction financially, and CO calculates profitability—all in real-time, with consistent, shared data. This comprehensive integration prevents operational silos, reduces delays, and improves decision-making across the entire organization.

Lesson Summary:
You’ve thoroughly examined how SAP ERP modules collectively manage specific business processes efficiently within complex global enterprises like PepsiCo. Each module—SD, MM, PP, FI, CO, HCM, WM, QM, and PM—plays a distinct yet interconnected role, ensuring streamlined, coordinated business operations. The seamless real-time data integration between these modules is critical in maintaining Pepsi’s operational efficiency and market responsiveness.
Lesson Takeaways:
-
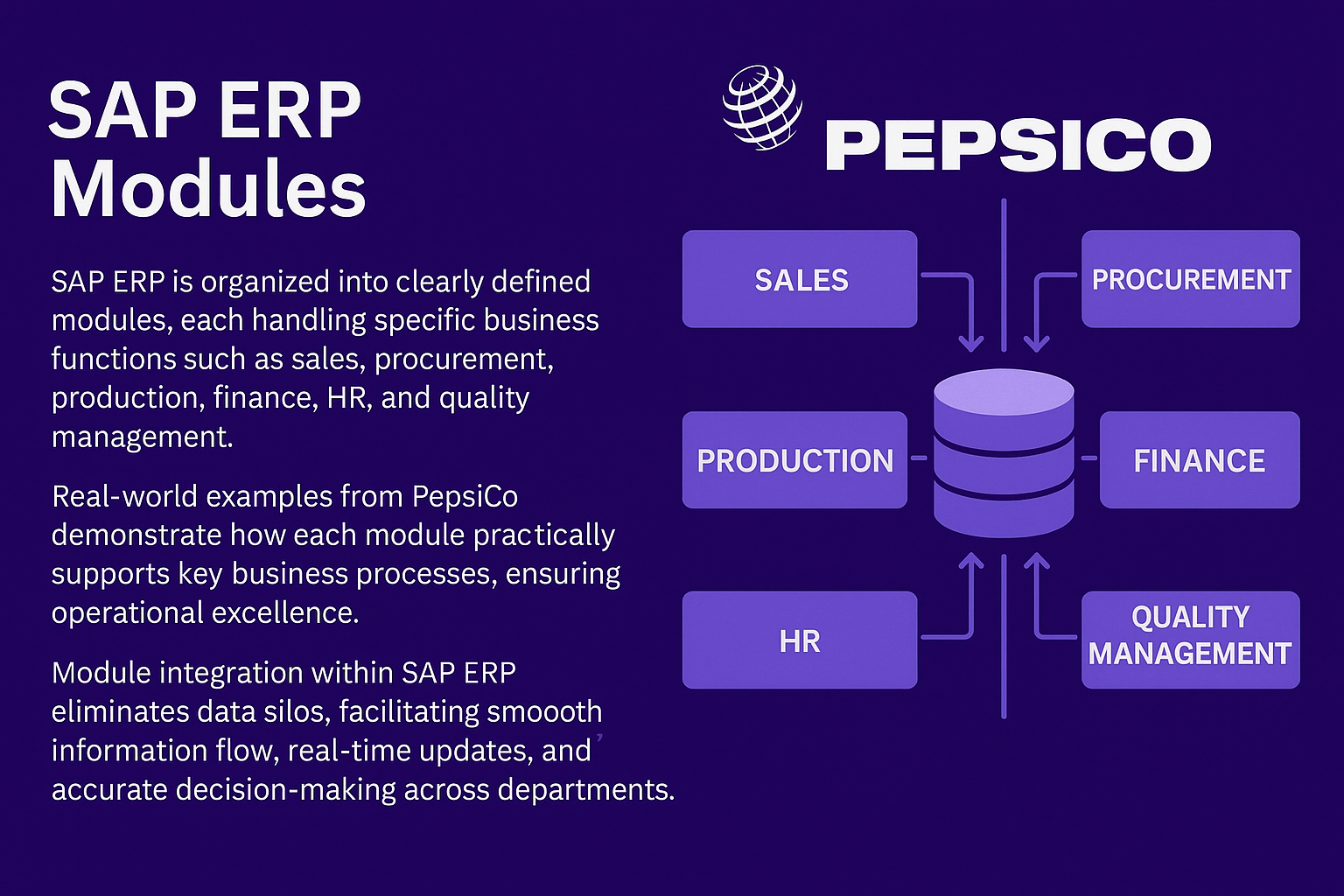
SAP ERP is organized into clearly defined modules, each handling specific business functions such as sales, procurement, production, finance, HR, and quality management.
-
Real-world examples from PepsiCo demonstrate how each module practically supports key business processes, ensuring operational excellence.
-
Module integration within SAP ERP eliminates data silos, facilitating smooth information flow, real-time updates, and accurate decision-making across departments.
-
Understanding SAP modules and their integrated functionality is crucial for grasping how large global businesses like PepsiCo manage complex operations efficiently.