Lesson Title: Creating and Managing Material Master Records in SAP ERP

Lesson Description:
In this practical session, you’ll master the essential skills needed to effectively create and maintain Material Master records in SAP ERP’s Materials Management module. You’ll learn how to accurately input purchasing details, define precise storage locations, configure critical accounting information, and establish valuation and pricing data. These records directly support procurement planning, inventory accuracy, warehouse management, and reliable financial reporting—foundations for operational efficiency and strategic decision-making.
To understand the impact of Material Master records, consider Pepsi’s global operations. Pepsi manages vast quantities of raw materials, packaging, and components required for beverage production and distribution worldwide. Accurate Material Master data ensures Pepsi can effectively control procurement, minimize inventory discrepancies, and make informed, timely financial decisions. When a Pepsi bottling facility orders packaging, detailed material records—covering everything from purchasing groups to storage bins—ensure correct orders, timely receipts, and seamless inventory updates.
Reflect on your own business environment as you learn: Could clearer and more detailed material data significantly improve your procurement accuracy and inventory management? Let’s now delve into SAP ERP’s material creation process and see how each piece of data influences business outcomes.
Lesson Learning Objectives:
-
Accurately create and configure new Material Master records in SAP ERP.
-
Understand the impact of key data fields such as purchasing groups, storage locations, valuation, and pricing.
-
Recognize how precise material data enhances procurement efficiency, inventory accuracy, and financial control.
-
Apply learned concepts to real-world scenarios, optimizing your organization’s operational effectiveness.
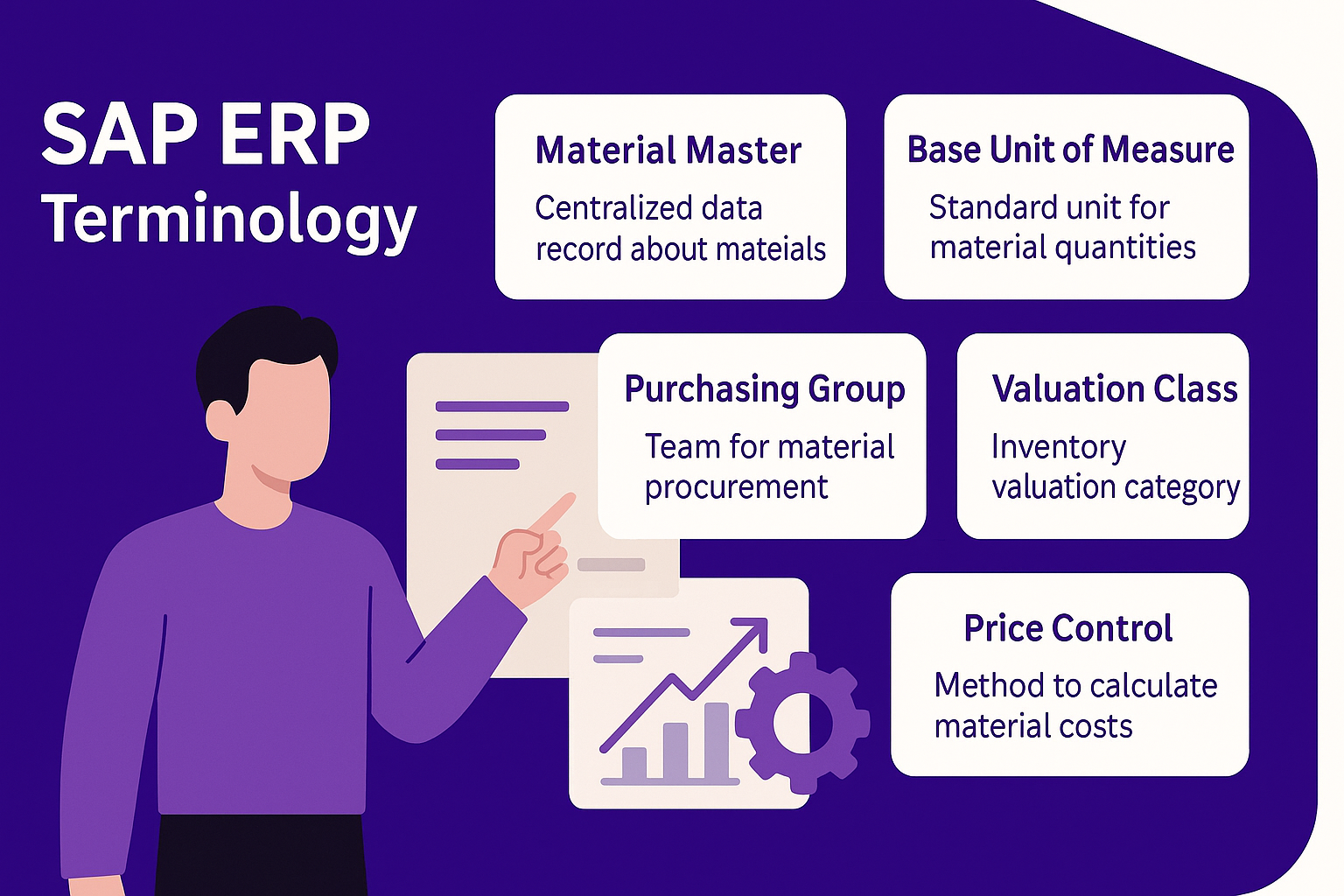
Terminology:
-
Material Master: Centralized data record containing key information about materials used within an organization.
-
Base Unit of Measure: The standard unit in which material quantities are tracked.
-
Purchasing Group: Team responsible for material procurement.
-
Valuation Class: Accounting category used for inventory valuation.
-
Price Control: Method used by SAP to calculate material costs (e.g., moving average price).
Lesson Key Points:
✅ Step-by-Step Material Creation Process:
To create a Material Master record, follow a structured procedure in SAP ERP:
-
Navigation Path: Start at the SAP Easy Access menu → Logistics → Materials Management → Material → Master → Material → Create General (transaction code MM01).
-
Material Number: Enter a unique identifier, enabling clear tracking and management of each material.
-
Industry Sector and Material Type: Choose “Mechanical Engineering” and “Raw Material” to define industry context and indicate material source clearly.
-
Selecting Views: Choose relevant views such as Basic Data, Purchasing, Purchase Order Text, General Plant Data Storage, and Accounting for comprehensive data entry.
✅ Entering Essential Material Data:
Carefully enter details within each selected view:
-
Basic Data View: Provide a clear description (“Pump Gasket”), base unit of measure (“PC”), material group (“Mechanics”), gross weight (“1 kg”), ensuring accurate identification and logistics management.
-
Purchasing View: Enter purchasing group (“01”), goods receipt processing time (“11 days”), and purchasing value key (“1”) to streamline procurement processes and ensure efficient communication with suppliers.
-
Purchase Order Text View: Clearly communicate specific procurement instructions, ensuring vendors deliver precisely to specifications, e.g., “Material supplied must strictly follow technical specification X30.”
-
General Plant Data Storage View: Enter storage location and bin (“BL01”) to precisely manage inventory location, aiding efficient warehouse operations.
-
Accounting View: Assign valuation class for raw materials, select price control method (“V” for Moving Average Price), and set the moving price (“20 euros”) to dynamically track and adjust material costs based on real-time procurement data.

✅ Impact of Accurate Material Master Data:
Accurate data entry significantly influences organizational effectiveness:
-
Enhances procurement efficiency by enabling clear supplier instructions and accurate purchasing decisions.
-
Supports precise inventory tracking, reducing stock discrepancies and facilitating timely inventory replenishments.
-
Improves warehouse management with clearly defined storage locations and bins, speeding up logistics processes.
-
Strengthens financial control by ensuring correct valuation and pricing, directly impacting financial reporting accuracy and strategic decisions.
✅ Practical Business Example (Pepsi):
At Pepsi, meticulous Material Master records underpin global supply chain efficiency:
-
Clear purchasing data enables rapid procurement adjustments.
-
Precise inventory information ensures optimal stock levels, preventing production delays.
-
Defined valuation methods maintain accurate financial reporting and cost control across international operations.
Pepsi’s success in managing vast global supply chains demonstrates the critical importance of precise, comprehensive Material Master records.
Lesson Summary:
You’ve successfully learned how to create and maintain detailed Material Master records within SAP ERP. Through practical steps, you’ve entered crucial purchasing details, established storage locations, and configured accounting information. Accurate Material Master data is foundational for operational efficiency—impacting procurement effectiveness, inventory accuracy, logistics management, and financial control.

Reflecting on Pepsi’s global practices highlights the real-world significance of this process. Precise data enables businesses to react rapidly, manage costs effectively, and ensure smooth operational flows across extensive supply chains.
Lesson Takeaways:
-
Comprehensive Material Master records directly enhance operational efficiency and procurement accuracy.
-
Precise data input, from purchasing group details to valuation class assignments, significantly influences financial outcomes and inventory management.
-
Real-world applications, such as Pepsi’s operations, illustrate how well-maintained Material Master data supports strategic decision-making, global coordination, and robust financial controls.

Consider your organization: Could implementing these detailed data practices reduce errors, streamline operations, and improve financial results? You’re now equipped to enhance your organization’s efficiency and effectiveness with robust Material Master data management. Keep applying these skills, and you’ll positively impact both operational success and strategic planning in your business.