Lesson Title: History and Evolution of SAP ERP
Lesson Description:
In this lesson, you’ll explore the history and evolution of SAP ERP, from its humble beginnings as a small startup in Germany to its position today as a global leader in business software. By tracing SAP’s journey, you’ll understand how its historical milestones directly influenced the features and functionality of SAP ERP ECC, now widely used by major corporations worldwide, including PepsiCo.

Lesson Learning Objectives:
-
Understand SAP’s foundational history and key milestones.
-
Explore the evolution from SAP R1 through SAP R3, ECC, and finally S/4HANA.
-
Appreciate how SAP’s historical innovations shaped today’s ERP systems.
Terminology:
-
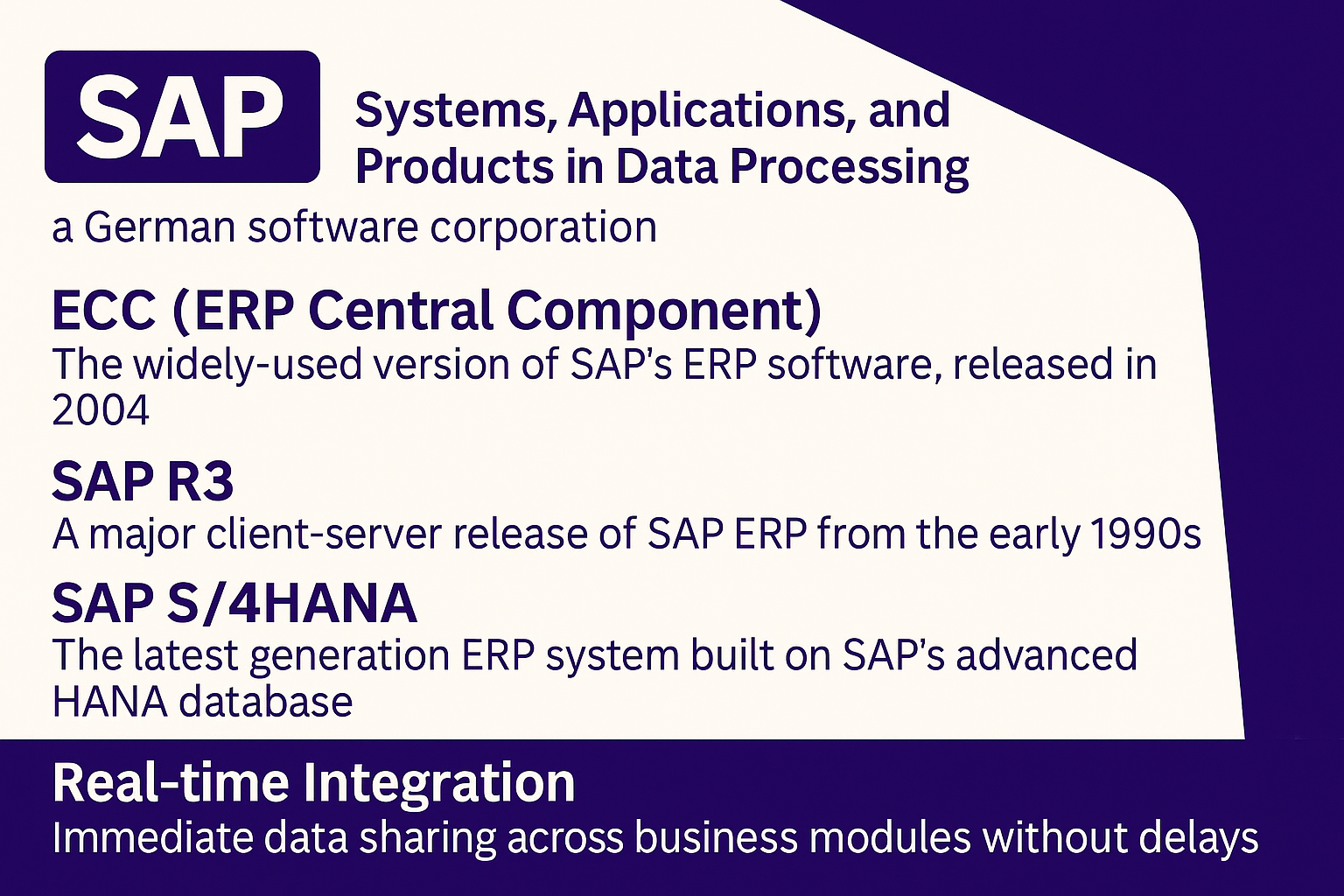
SAP: Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing—a German software corporation.
-
ECC (ERP Central Component): The widely-used version of SAP’s ERP software, released in 2004.
-
SAP R3: A major client-server release of SAP ERP from the early 1990s.
-
SAP S/4HANA: The latest generation ERP system built on SAP’s advanced HANA database.
-
Real-time Integration: Immediate data sharing across business modules without delays.
Lesson Key Points:
✅ Founding and Early Innovations:
-
Founded in Germany in 1972 by five former IBM engineers, SAP initially introduced a revolutionary real-time financial accounting software called R1.
-
Early innovations allowed immediate data sharing across company departments, significantly ahead of industry standards at the time.
✅ Evolution through R2 and R3:
-
SAP R2 (1979) expanded integration capabilities, attracting large multinational corporations.
-
SAP R3 (1991) was a transformative client-server ERP solution offering a graphical user interface, making the software easier and more accessible for companies worldwide.
✅ Emergence of SAP ECC:
-
SAP ECC, released in 2004, became a comprehensive solution managing finance, sales, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, and more in a single, integrated platform.
-
ECC’s robust integration attracted companies like PepsiCo, Coca-Cola, and General Motors, standardizing their global business operations.
✅ The Digital Shift with SAP S/4HANA:
-
Introduced in 2015, SAP S/4HANA utilizes SAP’s advanced in-memory database, enabling much faster data processing, real-time analytics, cloud capabilities, and modern user interfaces.
-
Today, S/4HANA helps businesses manage emerging technological trends, such as big data analytics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and mobile integration.

Lesson Summary:
You’ve traced SAP’s remarkable journey, recognizing how each innovation—from real-time data integration in R1 and R2 to the transformative client-server architecture of R3 and robust capabilities of ECC—has positioned SAP as the enterprise software leader. SAP’s evolution underscores its lasting relevance and explains why global enterprises continue to trust SAP ERP for their essential business operations.

Lesson Takeaways:
-
SAP’s historical progression directly influenced modern ERP systems, with each innovation building upon previous successes to create the comprehensive platform we use today.
-
SAP ECC remains widely trusted due to its reliability, extensive functionality, and proven effectiveness in integrating complex business operations globally.
-
The transition to SAP S/4HANA illustrates SAP’s continuous evolution, adapting to technological advancements like cloud computing, big data analytics, and real-time operational insight.
-
Understanding SAP’s history gives context to why its ERP system emphasizes real-time integration, centralized data management, and seamless cross-departmental communication.
