Lesson Title: Evolution and History of SAP
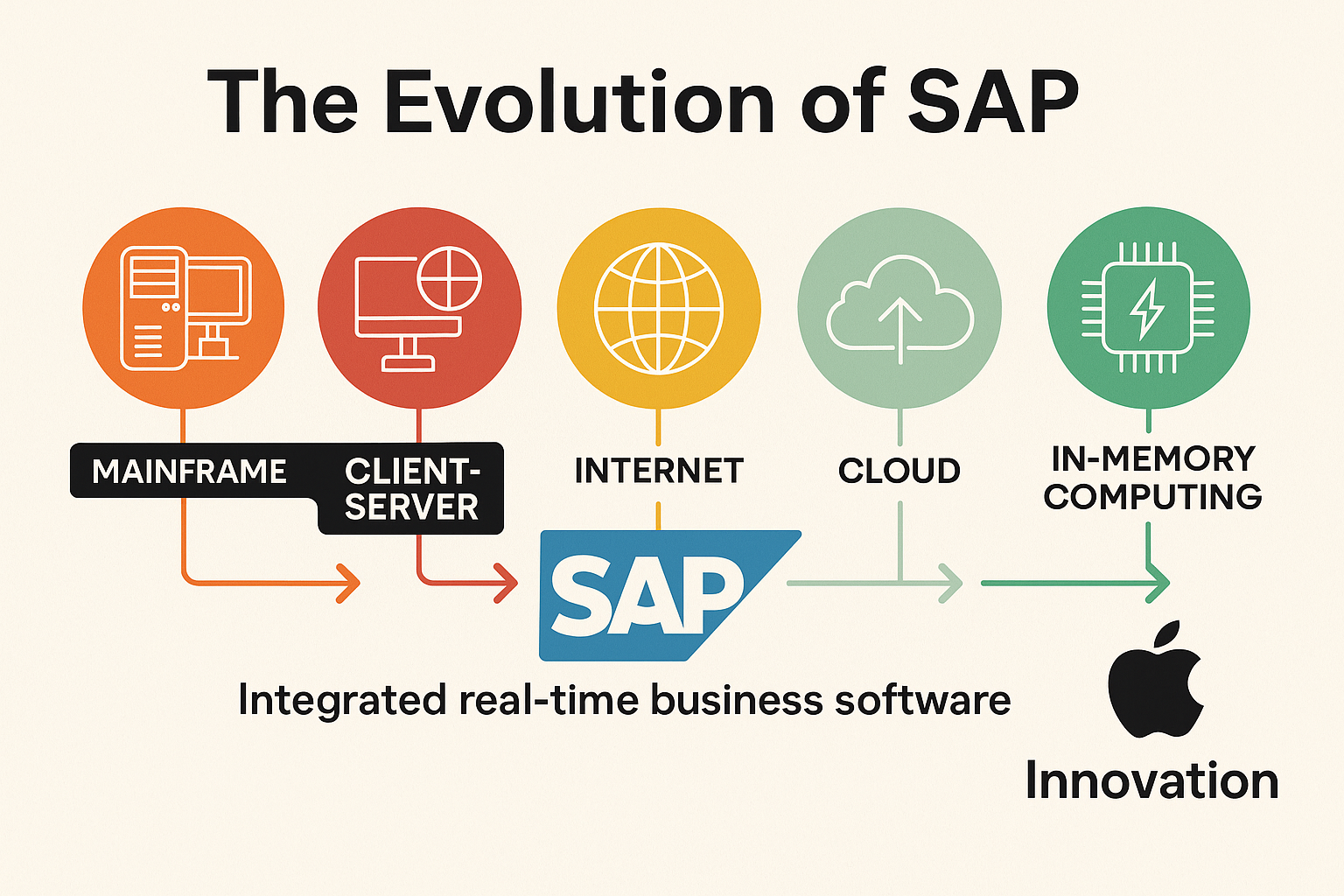
Lesson Description: In this lesson, you will explore the history and evolution of SAP, the company whose software became synonymous with ERP. Starting from its beginnings in 1972 to its current status as a leading global business software provider, we’ll trace SAP’s journey alongside technological advancements, highlighting key milestones and innovations.
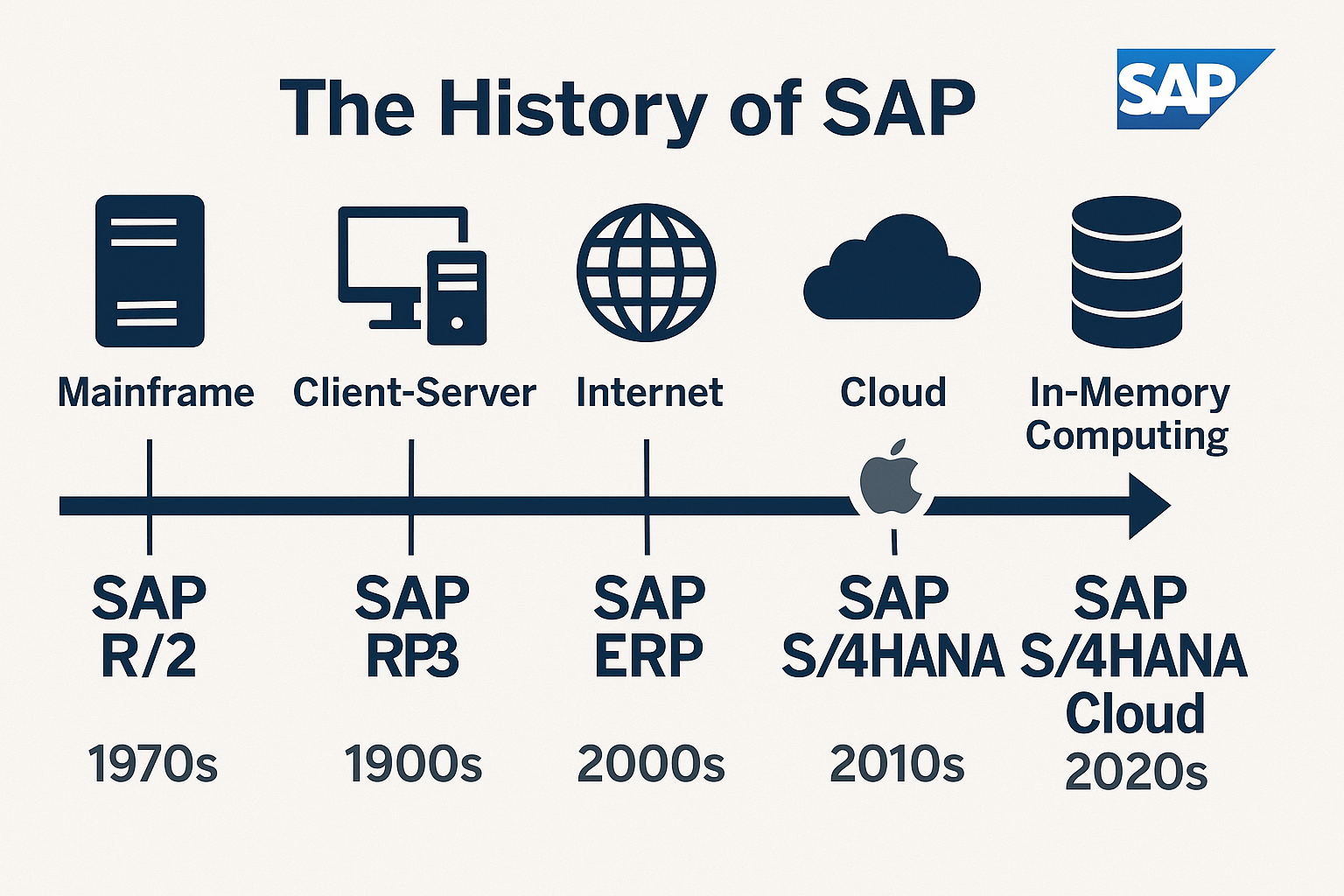
Lesson Learning Objectives:
-
Understand the origins and foundational concepts behind SAP.
-
Recognize key milestones in SAP’s growth and technological evolution.
-
Identify how historical developments influenced modern ERP systems like SAP S/4HANA Cloud.
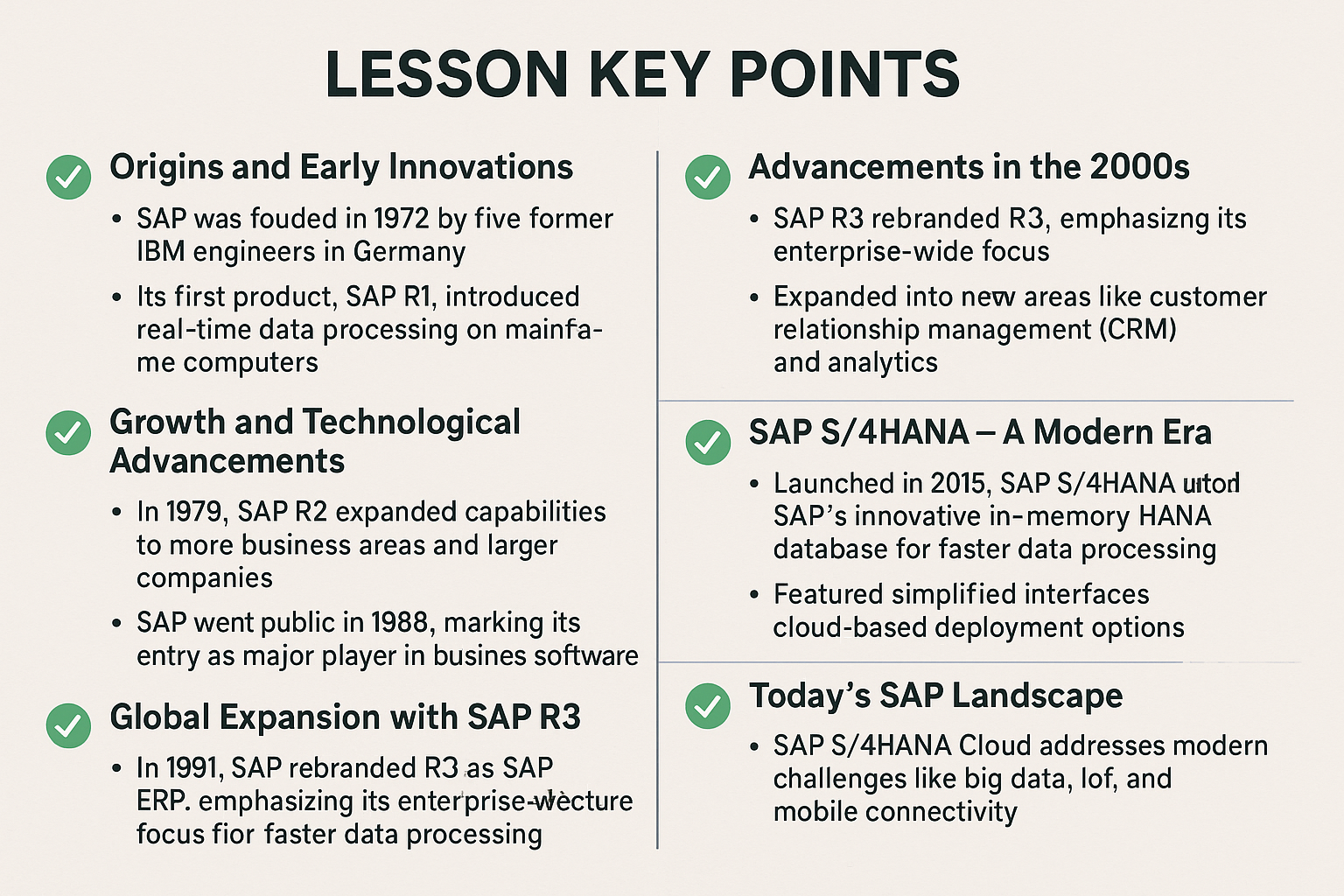
Lesson Key Points:
✅ Origins and Early Innovations:
-
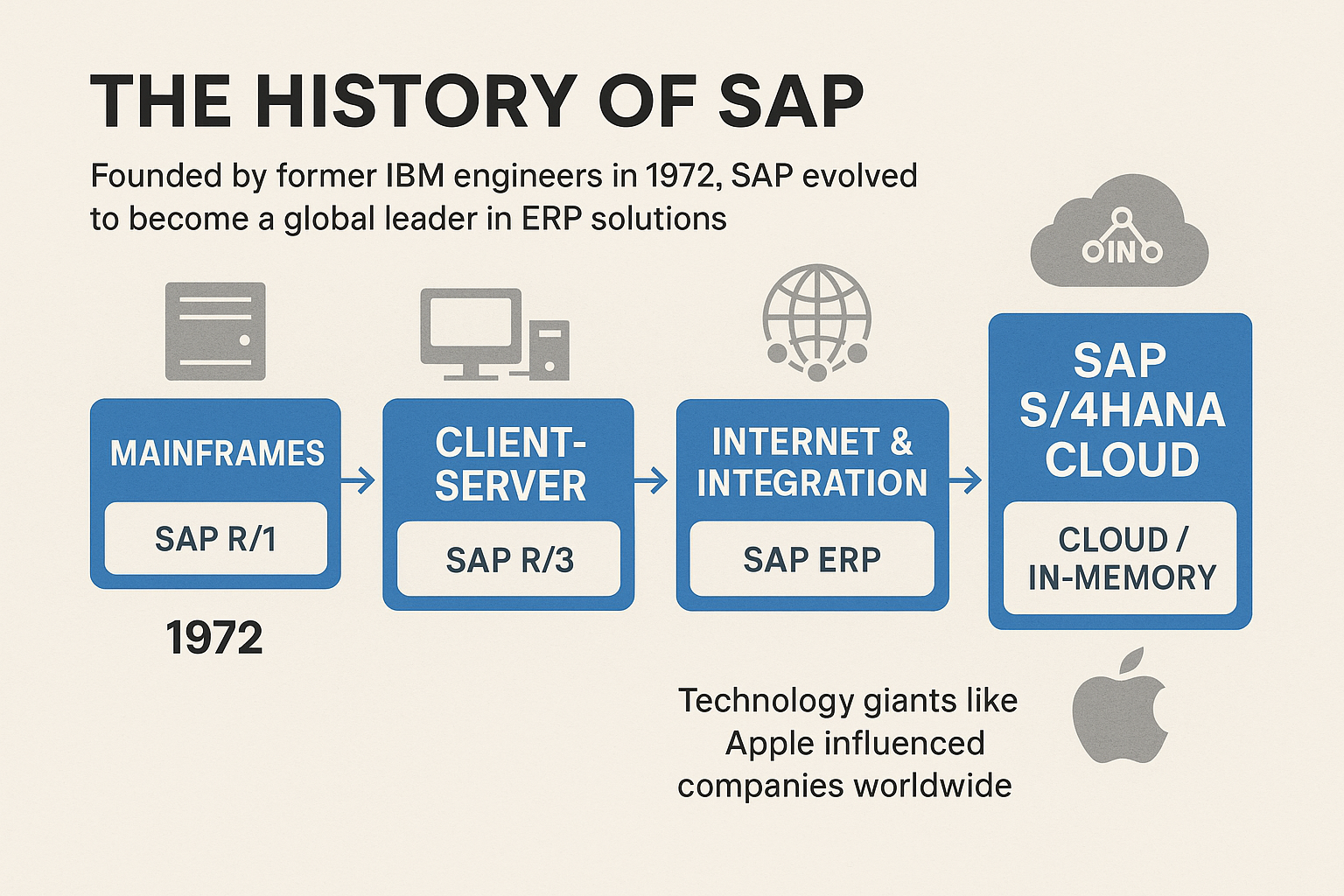
SAP was founded in 1972 by five former IBM engineers in Germany.
-
Its first product, SAP R1, introduced real-time data processing on mainframe computers.
✅ Growth and Technological Advancements:
-
In 1979, SAP R2 expanded capabilities to more business areas and larger companies.
-
SAP went public in 1988, marking its entry as a major player in business software.
✅ Global Expansion with SAP R3:
-
Introduced in 1991, SAP R3 featured a client-server architecture and a graphical user interface, significantly boosting accessibility and adoption worldwide.
✅ Advancements in the 2000s:
-
SAP rebranded R3 as SAP ERP, emphasizing its enterprise-wide focus.
-
Expanded into new areas like customer relationship management (CRM) and analytics.
✅ SAP S/4HANA – A Modern Era:
-
Launched in 2015, SAP S/4HANA utilized SAP’s innovative in-memory HANA database for faster data processing.
-
Featured simplified interfaces and cloud-based deployment options.
✅ Today’s SAP Landscape:
-
SAP S/4HANA Cloud addresses modern challenges like big data, IoT, and mobile connectivity.
-
Continues evolving to meet digital transformation needs with regular innovations and updates.
Lesson Summary: This lesson explored the history of SAP, from its inception by former IBM engineers in 1972 to becoming a global leader in ERP solutions. SAP evolved through key technological eras—mainframes (SAP R1 and R2), client-server (SAP R3), internet and integration (SAP ERP), and cloud/in-memory computing (SAP S/4HANA Cloud). Each innovation was driven by businesses’ changing needs for efficiency, real-time data processing, and strategic decision-making. SAP’s continuous reinvention kept it at the forefront of the business software industry, influencing companies worldwide, including technology giants like Apple.

Lesson Takeaways:
-
SAP’s innovative approach to integrated real-time business software transformed enterprise operations globally.
-
Each technological shift (mainframe, client-server, internet, cloud, in-memory computing) offered new capabilities, allowing SAP to remain relevant and valuable.
-
SAP’s commitment to ongoing innovation has enabled businesses, including leading companies like Apple, to stay competitive and agile in rapidly changing environments.
-
Understanding SAP’s history provides essential context for appreciating the design, functionality, and strategic value of modern ERP systems like SAP S/4HANA Cloud.