Lesson Title:
Retail Industry, Segments, and Process Overview
Lesson Description:
Welcome to the SAP for Retail Bootcamp! Imagine navigating a vast and complex marketplace without understanding the foundational structure—it could lead to confusion, inefficiency, and missed opportunities. The retail industry, pivotal to daily consumer experiences, bridges manufacturers and consumers through diverse channels. This lesson introduces you to the retail industry’s expansive landscape, key market segments, and essential business processes. You will understand the strategic importance of these elements and how they enable retailers to succeed in today’s competitive market.
Lesson Learning Objectives:
-
Clearly understand the role and significance of the retail industry.
-
Identify and differentiate between various retail market segments and distribution channels.
-
Comprehend critical business processes vital to successful retail operations.
-
Relate theoretical concepts to practical scenarios faced by modern retailers.
-
Recognize how strategic retail processes and segments align to achieve organizational goals.
Terminology:
-
Retail Industry: Sector focused on selling consumer goods and services directly to consumers.
-
Distribution Channels: Pathways through which goods and services reach consumers (physical stores, e-commerce, mobile applications).
-
Merchandising: The promotion and sales strategies used in retail.
-
E-commerce: Online buying and selling of goods and services.
-
Omni-channel: Integrated approach providing seamless customer experiences across multiple retail channels.
-
Consumer Goods: Products purchased for personal or household use.
Lesson Key Points:
-
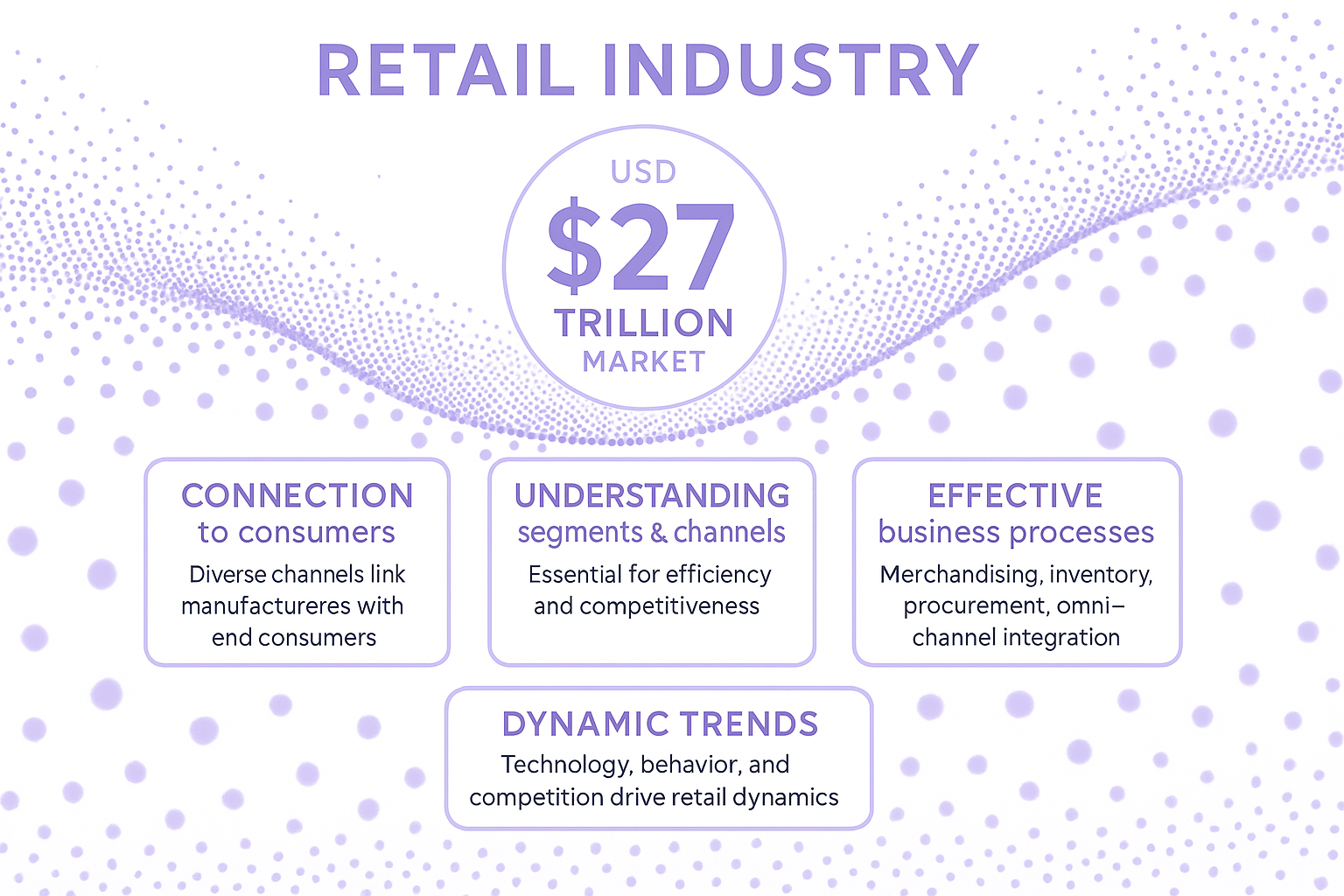
The retail industry significantly impacts the global economy, representing an estimated USD 27 trillion market.
-
Retail serves as a crucial connection between manufacturers and end consumers through diverse channels.
-
Comprehensive understanding of retail segments and distribution channels is essential for operational efficiency and competitive advantage.
-
Effective business processes in retail include merchandising, inventory management, procurement, and omni-channel integration.
-
Retail dynamics are continuously influenced by technological advancements, consumer behavior, and market competition.
Lesson Summary:
In this foundational lesson, we explored the retail industry’s dynamic nature, highlighting its key segments, distribution channels, and critical business processes. We emphasized the importance of understanding retail as a vital link between manufacturers and consumers, discussed its economic significance, and explored essential operational processes. Retailers equipped with this knowledge are better positioned to adapt and thrive amidst ongoing industry transformations.
Lesson Takeaways:
-
Understanding the retail industry’s landscape and structure is fundamental for successful retail operations.
-
Awareness of retail segments and distribution channels enables better strategic decision-making.
-
Mastery of core retail processes such as merchandising and omni-channel strategies significantly enhances operational effectiveness and market competitiveness.
-
Strategic alignment of retail operations with evolving consumer trends and technological innovations ensures sustained success and adaptability.